Specification
| Specification |
RTA- 100VDE | RTA-125VDE | RTA-170VDE | RTA-200VDE |
RTA-210VDE |
RTA-220VDE |
||
| Table Diameter | mm |
Ø100 |
Ø125 |
Ø200 | Ø250 | Ø320 | Ø400 | |
| Table Surface Height(Horizontal) | mm | 215 | 240 | 205 | 215 | 235 | 240 | |
| Reference Hole Diameter |
mm | Ø40H7 | Ø42H7 | Ø45H7 | Ø60H7 | Ø90H7 | Ø165H7 | |
| Table Width | mm | - | 12H7 | 12H7 | 12H7 | 14H7 | 14H7 | |
| MIN. Increment | deg. |
0.001° | 0.001 ° | 0.001 ° | 0.001 ° | 0.001 ° | 0.001 ° | |
| Rotating Axis | Swing Angle |
360°
| 360° | 360° | 360° | 360° | 360° | |
| Max. Rotation Speed (Motor 3000 min-1) |
rpm | 62.5 | 62.5 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | |
| Gear Ratio
|
1/48 | 1/48 | 1/60 | 1/60 | 1/60 | |||
| Indexing Accuracy | arc-sec | 20 |
20 | 18 | 16 | 16 | 16 | |
| Repeatability Accuracy | arc-sec | 8 |
8 |
4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Servo Motor |
FANUC | αiF 2 βiS 4 |
αiF 2 βiS 4 |
αiF 4 βiS 8 |
αiF 8
βiS 12 |
αiF 12 βiS 22 |
αiF 12 βiS 22 |
|
| MITSUBISHI | HF75S | HF75S | HG104S | HG154S | HG204S | HG204S | ||
| SIEMENS | 1FK7034 | 1FK7060 | 1FK7060 | 1FK7063 | 1FK7083 | 1FK7083 | ||
| Tilting Axis | Swing Angle | |||||||
| Max. Rotation Speed (Motor 3000 min-1) | rpm | -90°~+110° |
-90°~+110°
|
-90°~+110°
|
-90°~+110°
|
-90°~+110°
|
-90°~+110°
| |
| Gear Ratio | 1/60 |
1/60
|
1/60
|
1/60
|
1/60
|
1/60
| ||
| Indexing Accuracy | arc-sec | 15 |
15
|
15
|
15
|
15
|
15
| |
| Repeatability Accuracy | arc-sec | 4 |
4
|
4
|
4
|
4
|
4
| |
| Servo Motor | FANUC | αiF 4+B βiS 8+B |
αiF 4+B βiS 8+B |
αiF 4+B βiS 8+B |
αiF 4+B βiS 8+B |
αiF 4+B βiS 8+B |
αiF 4+B βiS 8+B | |
| MITSUBISHI | HF104S+B |
HF104S+B
|
HF104S+B
|
HF104S+B
|
HF104S+B
|
HF104S+B
| ||
| SIEMENS | 1FK7060+B |
1FK7060+B
|
1FK7060+B
|
1FK7060+B
|
1FK7060+B
|
1FK7060+B
| ||
| MAX. Allowable Load on the Table | Level |
Kg | 30 | 90 | 160 | 190 | 250 | 960 |
| Tilt |
Kg | 90 | 180 | 320 | 380 | 500 | 1920 | |
| Net Weight(servo motor excluded) | Kg | 128 | 60 | 80 | 118 | 180 | 295 |
Feature
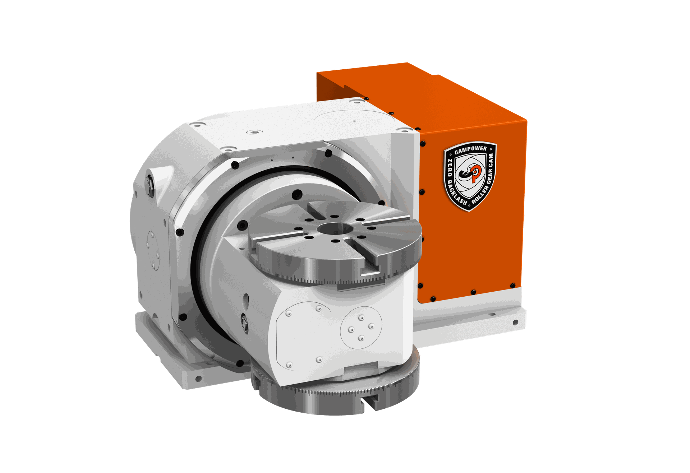
RTA series rotary table are used for high-precision and high-efficiency processing of complex workpieces, especially suitable for awrospace, automotive, mold manufacturing, and other applications requiring high precision.
As a sibling to the RTA series, the RTAD series is characterized by having two machining surfaces on inclined axes, which is particularly noteworthy as it allows for more efficient use of machining time and improved efficiency. It is worth noting that the RTAD series is the world's first specification, indicating its innovative and unique nature in the industry. The design with dual inclined axes makes this rotary table more suitable for applications requiring complex multi-dimensional machining, such as complex surface parts or special-shaped workpieces. This high level of innovation and versatility makes the RTAD series rotary table a compelling choice in the field of mechanical machining and manufacturing, especially for applications requiring high efficiency and high precision. This helps to improve product quality, shorten processing cycles, and enhance competitiveness.
Drive mode
Unlike the commonly used worm and gear mechanisms in the market, COMP Precision Machinery employs roller cam mechanisms for both the fourth and fifth axes to drive the machine.
Roller cam mechanisms and worm and gear mechanisms are two different mechanical structures, and they differ in terms of stability, rigidity, and wear and tear:
|
|
Roller Cam Mechanism | Worm and Gear Mechanism |
| Stability | Exhibits higher stability. The design of roller cams allows for smoother motion, reducing vibration and instability. |
Lower stability, with potential for vibration and uncertainty, especially under high loads or high-speed conditions. |
|---|---|---|
| Rigidity | Possesses higher rigidity, providing better resistance to external forces and torque. | Relatively softer, potentially experiencing some deformation when subjected to external forces. |
| Wear and Tear | Lower wear and tear, capable of maintaining high precision over extended periods. | May experience wear and tear due to friction on contact surfaces, particularly during prolonged high-frequency use. |
| Backlash | Typically achieves zero backlash, offering more accurate motion control. | May have some backlash, affecting precision and the accuracy of motion. |
Applications
Dimensions